Inflation, or rising prices, has been a frequent experience for both families and businesses during the past two years. In an effort to reduce inflation, central banks everywhere have raised interest rates. However, by decreasing the purchasing power of consumers and businesses, the central banks' policies have drastically slowed down financial activity. As demand for loans decreased and banks continued to tighten requirements, bank lending to individuals and businesses has significantly decreased since June 2022. Rising bond yields and high interest rates are driving up the needed cost of capital, or discount rate, which is driving up equities prices. Bond rates and stock markets have an inverse connection, meaning that while yields are rising, stocks are heading in the opposite direction.
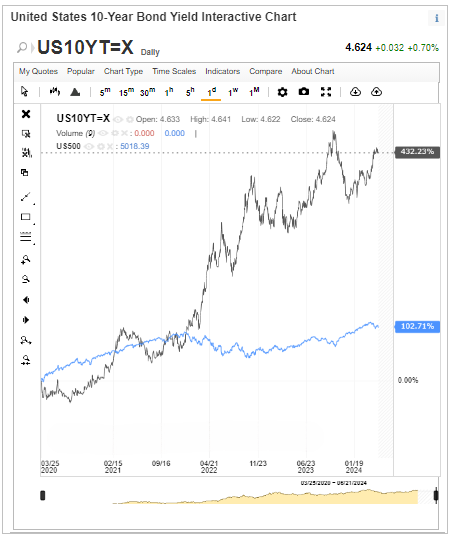
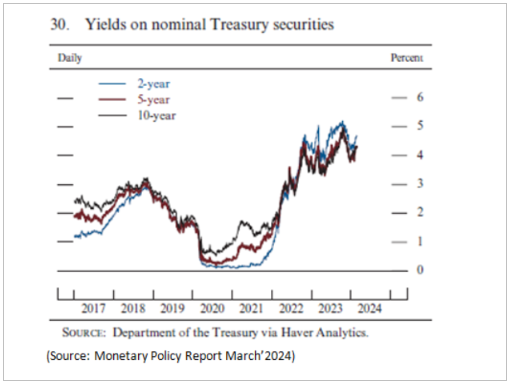
In 2023, yields on nominal long-term Treasury notes began to rise in the spring and continued to rise significantly until mid-October, when they abruptly reversed direction. The yield on a 10-year Treasury note peaked at roughly 5% and fell to just less than 4% by the end of the year. Longer-term nominal Treasury yields have risen thus far in 2024; by late February, the 10-year Treasury yield had grown to roughly 4.4%. The yield on the 10-year Treasury note is closely monitored as a gauge of overall investor confidence, despite being viewed as a risk-free investment. An key component in determining the interest rate on home mortgages is the yield on agency mortgage-backed securities (MBS), which saw a significant surge over the summer before declining again towards the end of 2023. The yields on agency MBS have risen thus far in 2024, standing in late February at levels notably above those in June 2023.
Since June, there has been a notable gain in the S&P 500 index, which is regarded as the finest single indicator of large-cap U.S. equities and represents around 80% of the market capitalization. As of April 30, 2024, the S&P 500 index had achieved an annualised price return of 20.78% during the previous year, reaching 5035.69 points. With the prospect of Federal Reserve rate reduction, the S&P 500 index rebounded towards the end of 2023 after seeing a significant loss over the late summer and early fall. Due mostly to the strength of industry heavyweights like Microsoft (NASDAQ: MSFT), NVIDIA Corp. (NASDAQ: NVDA), Amazon Inc. (NASDAQ: AMZN), etc., the overall equity prices are currently nearing historical highs. Small-cap indices have underperformed over the past year, despite the larger equity indices' strong performance.
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which wrapped up its most recent policy meeting on May 1, 2024, decided to keep interest rates at their current range of 5.25% to 5.50%. Even though inflation has significantly decreased over the previous year, the FOMC noted that it has not made much progress towards its 2% goal inflation and that inflation risks continue to be a worry. Following the announcement, the S&P 500 fell 97.78 points, to 5018.39 on May 1, 2024, from 5116.17 points on April 29, 2024. The S&P 500, however, finished 45.81 points higher at 506420. More recently, the economy's weakness in the face of increased interest rates was countered by the increase in consumer confidence brought about by improvements in real wage prospects. We think that the possibility of an extended period of upward inflation and rate.
The U.S. equity market's small-cap category is gauged by the S&P SmallCap 600® index, which saw a price return of 10.92% last year, ending at 1272.36 on May 1, 2024. On the other hand, small-cap firms have seen a rise in values recently due to anticipations of a looser monetary policy. Some of the losses in banking stocks that had been linked to pressures in the banking industry during the first half of 2023 have been reversed. While regional bank share prices only saw a minor pullback, the equity prices of the largest banks saw a return to their early 2023 levels. Up until late October, the VIX, which gauges the S&P 500® (SPX) expected volatility for the ensuing 30 days, grew somewhat, although subsequently declined to reach levels somewhat lower than those prevailing in early June, indicating a bullish sentiment.
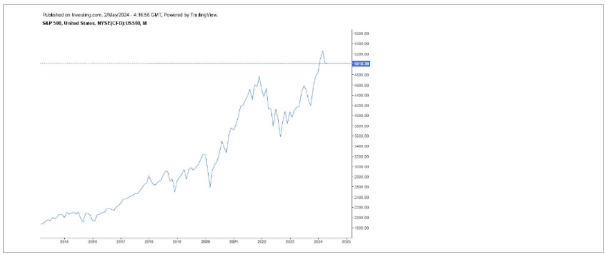
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which wrapped up its most recent policy meeting on May 1, 2024, decided to keep interest rates at their current range of 5.25% to 5.50%. Even though inflation has significantly decreased over the previous year, the FOMC noted that it has not made much progress towards its 2% goal inflation and that inflation risks continue to be a worry. Following the announcement, the S&P 500 fell 97.78 points, to 5018.39 on May 1, 2024, from 5116.17 points on April 29, 2024. The S&P 500, however, finished 45.81 points higher at 506420. More recently, the economy's weakness in the face of increased interest rates was countered by the increase in consumer confidence brought about by improvements in real wage prospects. We think that the possibility of an extended period of upward inflation and rate cuts by the Federal Reserve poses "higher-for-longer" risks that tend to favour value investing strategy vs. growth.

