By 2024, the artificial intelligence industry is expected to grow to a size of US$4.13 billion.
It is anticipated that the market would increase at a rate of 28.39% per year (CAGR 2024–2030) and reach a value of US$18.50 billion by 2030.
Comparatively speaking, the US market will be the largest worldwide, with US$50.16 billion in 2024.
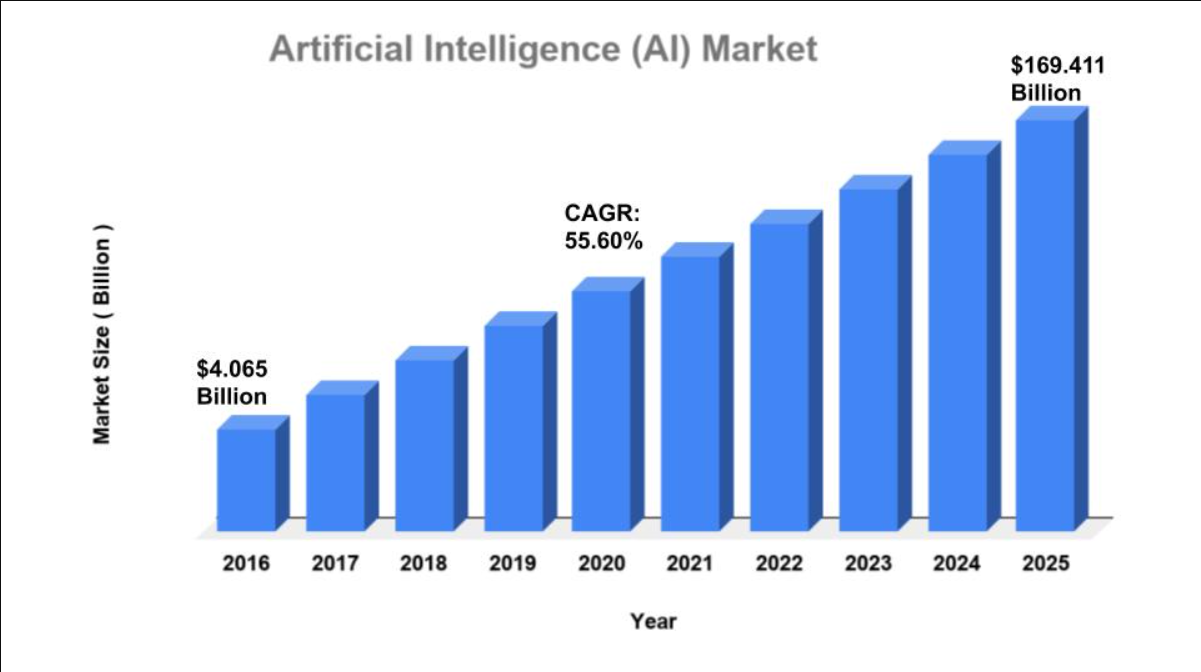
Source: ilu.valuates.com
The growing application of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare, especially in fields like drug discovery, personalised medicine, and disease diagnostics, is one of the current trends in the AI sector. Using AI to enhance customer support and service through chatbots and virtual assistants is another trend. Another emerging trend that makes it possible to handle AI applications more effectively and powerfully is the development of AI chips and edge computing. Lastly, it is anticipated that the AI industry will continue to expand and innovate due to the integration of AI with other technologies like blockchain and the Internet of Things (IoT).
The AI sector is expanding due to a number of factors. First, as AI algorithms need large amounts of data to learn and develop, the growing availability of big data is opening up new applications potential for AI. Second, the processing of AI applications is becoming more potent and efficient because to improvements in processing power and cloud computing infrastructure. Third, the adoption of AI technology is being propelled by the increasing need for automation and optimisation across a range of industries, including manufacturing, banking, and transportation. Fourth, the market for AI technology is growing as a result of the growing usage of AI in consumer-facing applications like chatbots and virtual assistants. The AI business is seeing growth and innovation due to the increasing alliances and investments among governments, academic institutes, and technological corporations.
Up until 2030, the artificial intelligence (AI) market is anticipated to increase significantly due to the increasing industry use of AI technologies, improvements in AI infrastructure and algorithms, and rising investment in AI research and development. It is anticipated that the industry will continue to grow and innovate, with artificial intelligence (AI) playing a bigger role in business processes and consumer-facing applications.
Artificial intelligence (AI) worldwide - statistics & facts
For some, the concept of artificial intelligence conjures up thoughts of their favourite sci-fi movie sequences, supercomputer helpers, and computers capable of creative thought. Though not quite as futuristic, the reality is not that unlike from this. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the capacity of a computer or machine to imitate the functions of the human mind, which frequently gains knowledge from prior experiences in order to comprehend and react to language, choices, and issues. The market for AI technology is enormous; it will likely reach a value of over 1.8 trillion dollars by 2030, up from a projected 200 billion dollars in 2023.
Source: zippia.com
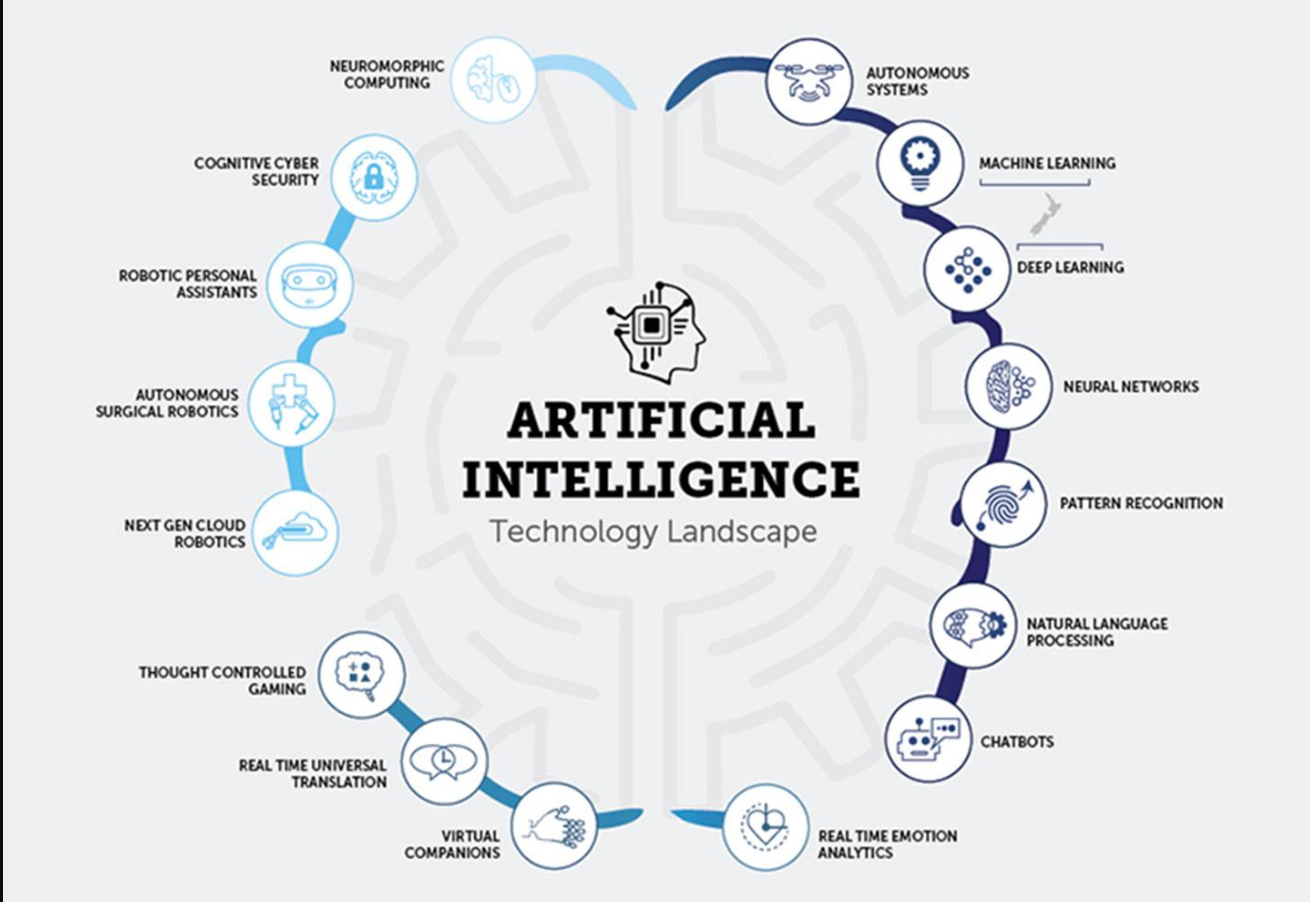
Artificial Intelligence has various forms.
Source: codingdojo.com
Deep learning and machine learning are the two main categories of AI. There are also more subcategories within these, including robotics, computer vision, natural language processing, and more. The most fundamental and straightforward type of AI is machine learning. Machine learning programmes are restricted in scope and given a very defined set of criteria to employ in human-machine interactions. It is also the most widely used type of AI, appearing in voice commands, apps, simple chat assistants, and other limited interactions.
Deep learning is more in line with human expectations for AI. AI starts with datasets and settings in deep learning programmes, but as it learns from humans, it can incorporate user data. In this sense, the AI becomes more advanced as it is employed in the process. Recent examples of advanced deep learning programs are OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Google’s Bard.
The use of generative AI has increased.
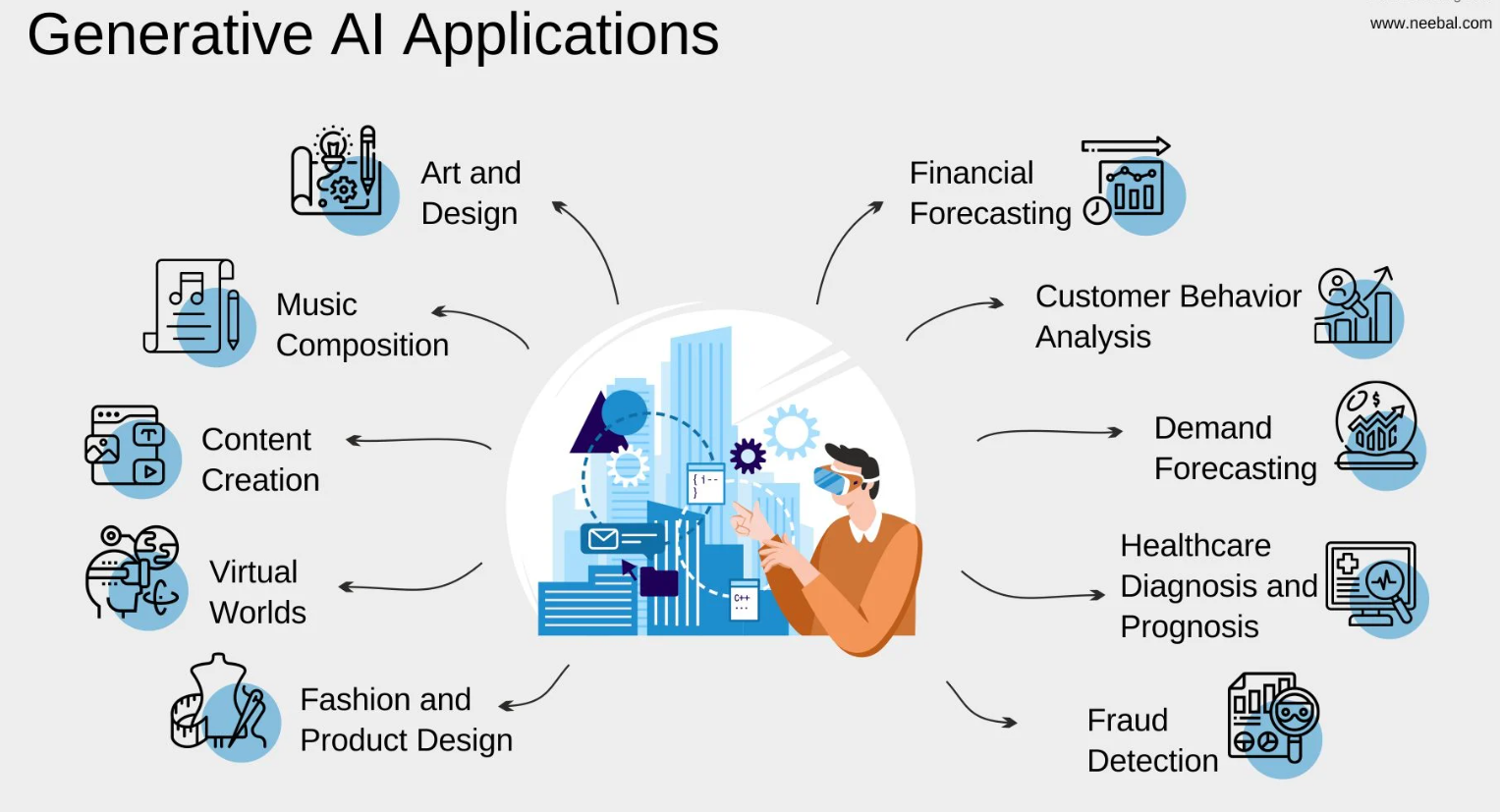
Source: neebal.com
The end of 2022 saw the rise to prominence of generative AI, a new paradigm in AI development. While these programmes are not really new—they have been around for the past five years—the progress in this area has been astounding. Programmes that can generate text, images, music, and other media are referred to as generative AI. Encouraged by the late 2022 publication of ChatGPT-3, the field has attracted the interest of Google, Microsoft, Amazon, and most recently, Elon Musk's X. Through a range of startup businesses, they are all vying to create the most sophisticated generative artificial intelligence. This development is not without problems, though, since generative AI firms have been charged with conditioning their AI models on writers and artists are ignored by copyrighted writings and visuals.
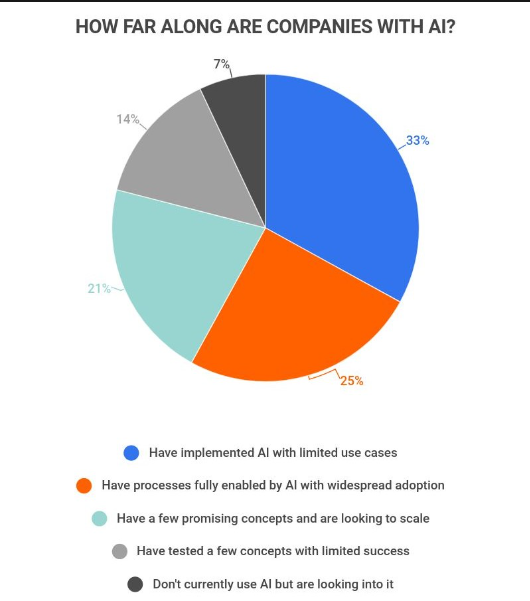
AI is moving forward at a rapid pace.
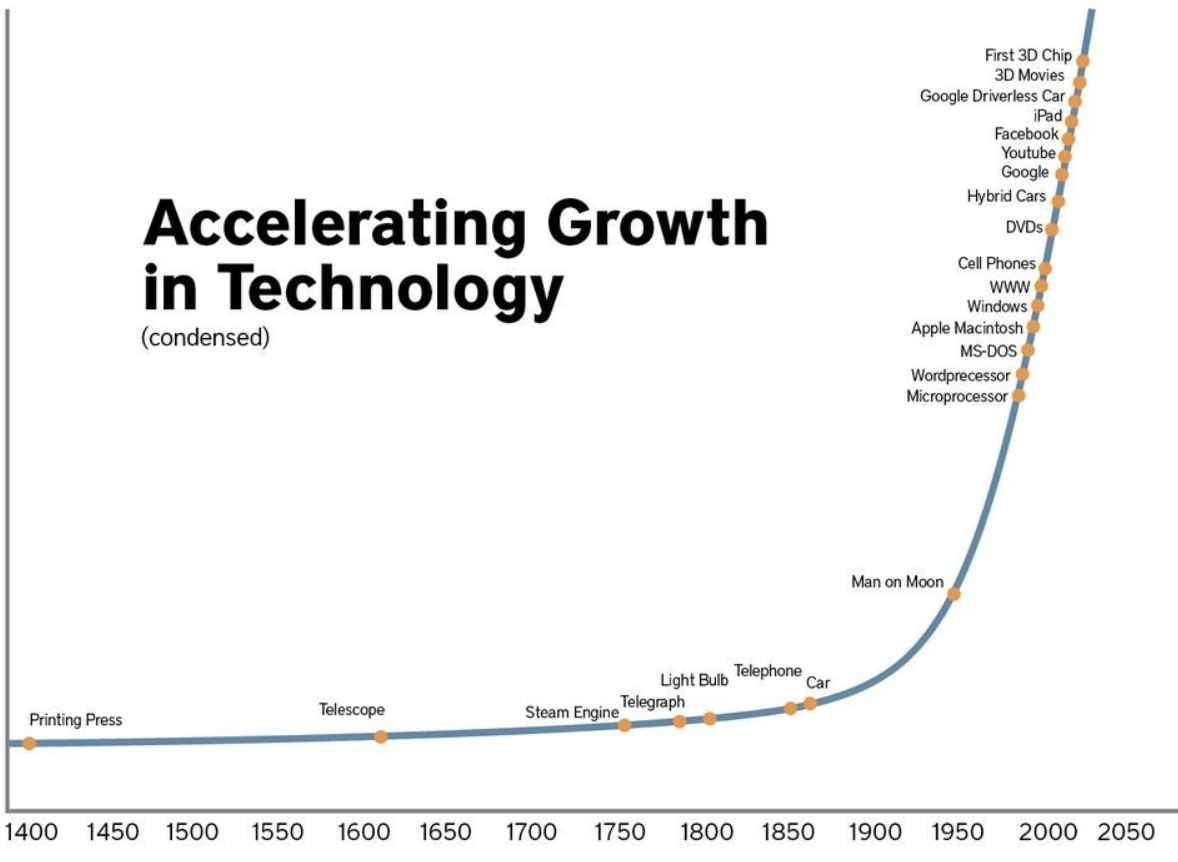
Source: jmtconsulting.com
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is predicted to remain competitive in all advanced economies due to the progress made in deep learning and machine learning, as well as the potential impact these programmes may have on the world economy. To avoid falling behind, any business hoping to gain an advantage over rivals would be wise to get involved early.
Market size and revenue comparisons for artificial intelligence (AI) from 2020 to 2030
Many sources predict that the artificial intelligence (AI) market will increase significantly during the next ten years. The AI market is expected to increase at a compound annual growth rate of 17.3% from 241.8 billion US dollars in 2023 to over 740 billion US dollars in 2030, according to Statista statistics. Meanwhile, Next Move Strategy Consulting projects that by 2030, its estimated 208 billion US dollars in value will have increased nine times, to reach 1.85 trillion US dollars. In fact, a wide range of industries, including marketing, healthcare, education, finance, and media, are covered by the AI market. Globally, the pace at which technology is being adopted and deployed is accelerating. Chatbots, AI that generates images, and mobile apps all of the key developments that will improve AI in the upcoming years.
AI requires information.
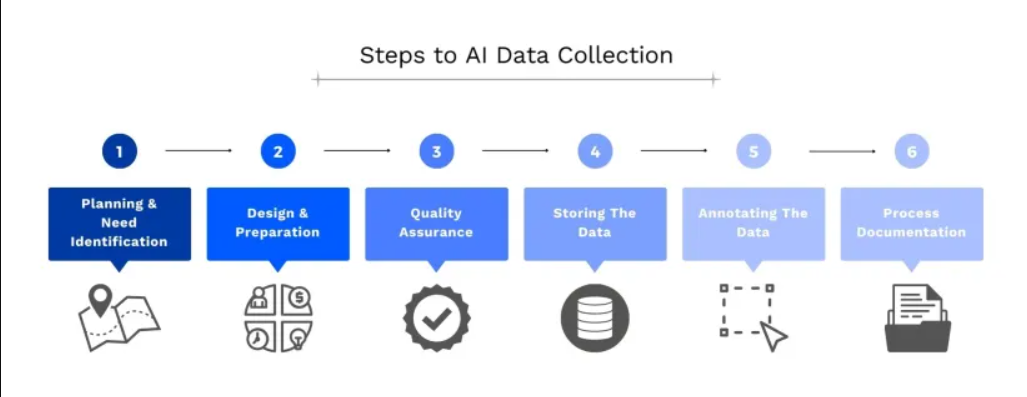
Source: research.aimultiple.com
The most challenging infrastructure-related issue associated to AI is still data management. For AI businesses, this is a multifaceted challenge. Some need more specialised data, while others struggle to keep the data their company already has organised and managed. The amount of data that can be held outside of national boundaries is regulated by major international organisations such as the US, China, and the EU. These organisations collectively provide formidable obstacles to data-hungry AI firms.
Artificial Intelligence could increase productivity.
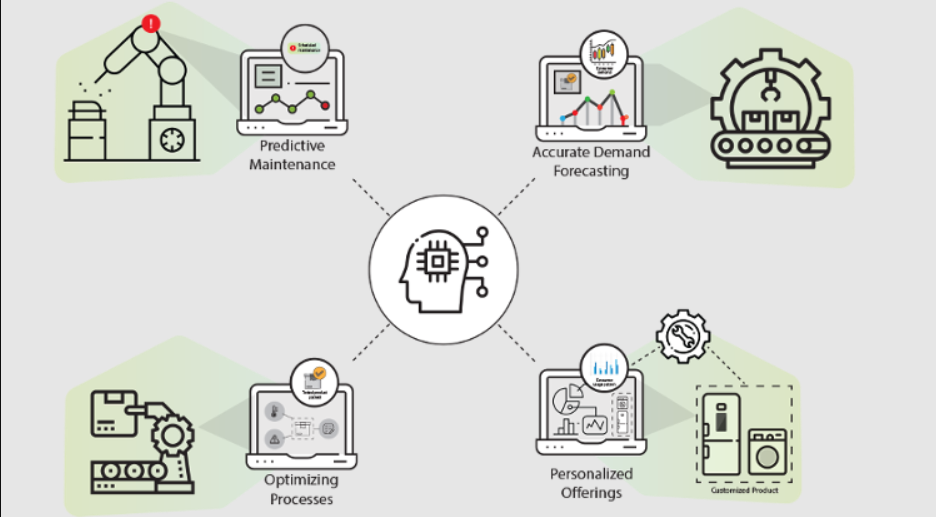
Source: volansys.com
The United States is probably going to be greatly impacted by the use of AI, both in terms of labour changes and productivity. This effect does not have to be entirely bad. If labour rotation is done properly, people can be quickly transferred from physical labour to more productive and value-added businesses. A more productive economy will result from these industry changes. In fact, over a ten-year period, AI might increase the growth in labour productivity in the US. Naturally, a number of variables will affect this, including the strength of the upcoming AI generation, the complexity of the activities it can accomplish, and the quantity of jobs it replaces.